

The dedicated Pawar Multispeciality Hospital is one of the best hospitals in Pune for Gall Bladder Surgery. The hospital conducts various Gall Bladder Surgeries.
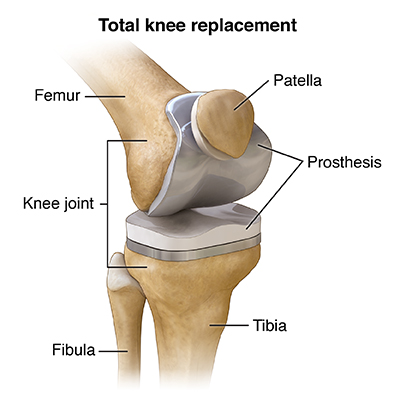
Arthroplasty is a surgical procedure to restore the function of a joint. A joint can be restored by resurfacing the bones. An artificial joint (called a prosthesis) may also be used. Various types of arthritis may affect the joints.
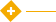
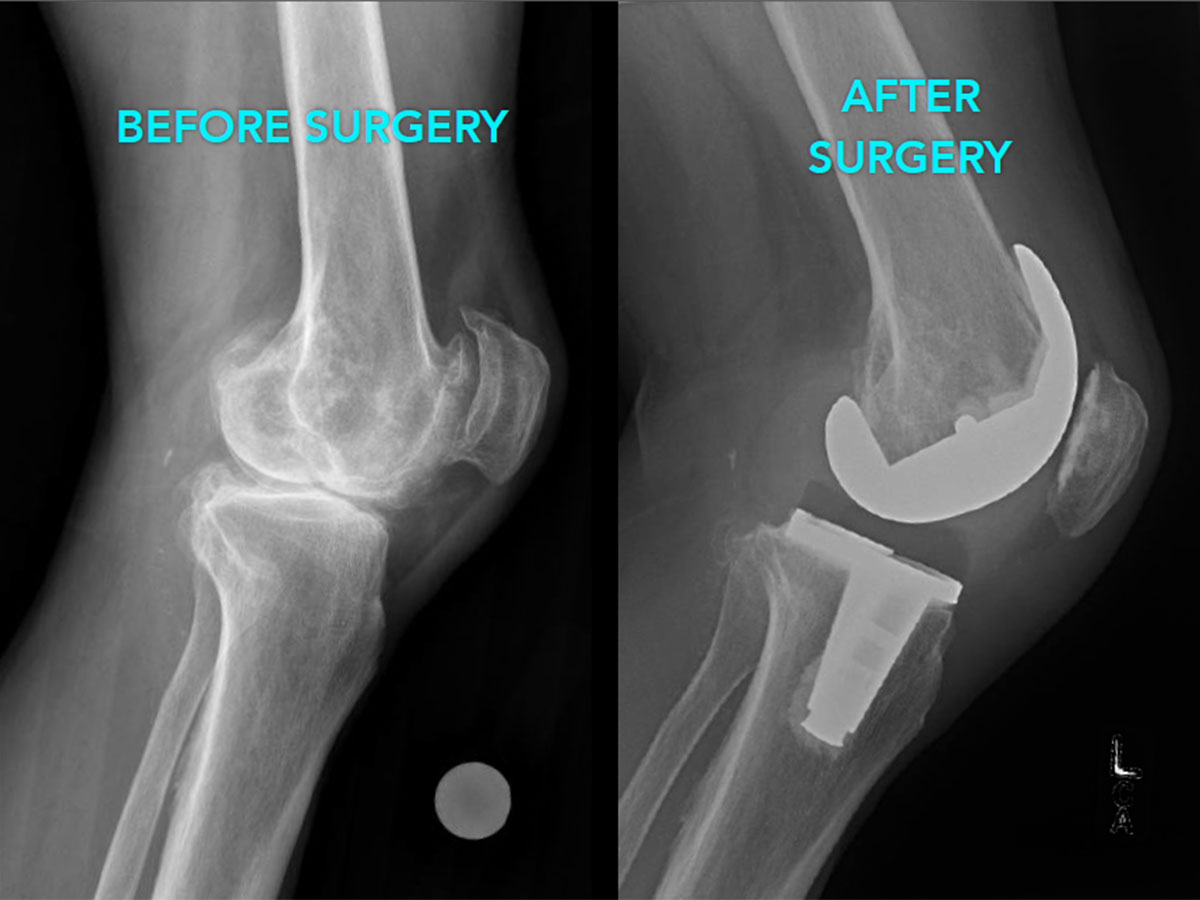
For the last 15 years the most successful and common form of arthroplasty is the surgical replacement of arthritic or destructive or necrotic joint or joint surface with a prosthesis. For example a hip joint that is affected by osteoarthritis may be replaced entirely (total hip arthroplasty) with a prosthetic hip. This would involve replacing both the acetabulum (hip socket) and the head and neck of the femur. The purpose of this procedure is to relieve pain, to restore range of motion and to improve walking ability, thus leading to the improvement of muscle strength.
Arthroplasty is surgery performed to relieve pain and restore range of motion by realigning or reconstructing a dysfunctional joint
The goal of arthroplasty is to restore the function of a stiffened synovial joint and relieve pain. As a surgical procedure, it is usually performed when medical treatment has not improved function in the affected joint. There are two types of arthroplastic surgery: joint resection and interpositional reconstruction. Joint resection involves removing a portion of the bone from a stiffened joint, increasing the space between the bone and the socket to improve the range of motion. Scar tissue eventually fills the gap, narrowing joint space again. Pain is relieved and motion is restored, but the joint is less stable.
Interpositional reconstruction is surgery to reshape the joint and add a prosthetic disk between the two bones forming the joint. The prosthesis can be made of plastic, metal, ceramic material, or formed from such body tissue as skin, muscle, or fascia. When interpositional reconstruction fails, total joint replacement may be necessary. Joint replacement is also called total joint arthroplasty.
In recent years, joint replacement has become the operation of choice for most chronic knee and hip problems, particularly because of advances in the type and quality of prostheses (articifical joints). Elbow, shoulder, ankle, and finger joints are more likely to be treated with joint resection or interpositional reconstruction.
Arthroplasty is performed on people suffering from severe pain and disabling joint stiffness. Osteoarthritis (OA), a degenerative joint disease, is the most common condition causing joint destruction with pain and impaired movement. Other causes include rheumatoid arthritis (RA), hemophilia, synovitis, and rare bone diseases, which are all known to destroy cartilage. Joint resection, rather than joint replacement, is more likely to be performed on people with rheumatoid arthritis, especially when the elbow joint is involved. Joint replacement is usually reserved for older patients, because of the limited longevity of benefits. The younger the patient, the greater the reliance on medical treatment.
Arthroplasty is performed under general (affecting the entire body) or regional (numbing a specific area of the body, such as spinal block) anesthesia in a hospital, by an orthopedic surgeon. Although many hospitals and medical centers perform common types of joint surgery, orthopedic hospitals that specialize in joint surgery tend to have higher success rates than less specialized centers
In joint resection, the surgeon makes an incision at the joint, then carefully removes the minimum amount of bone necessary to allow free motion. The more bone that remains, the more stable the joint. Ligament attachments are preserved as much as possible. In interpositional reconstruction, both bones of the joint are reshaped, and a disk of material is placed between the bones to prevent their rubbing together. Length of hospital stay depends on the joint affected; in the absence of complications, a typical stay is only a few days.
Significant disabling pain, deformity, and reduced quality of life are the primary indications for arthroscopic procedures. Patients at this stage of discomfort and disability will most likely have already been diagnosed with a form of arthritis. Pain and stiffness on weight-bearing joints are the major symptoms that patients report, though some people experience night pain as well. Other symptoms may include stiffness, swelling, and locking of the joint; and even the joint giving way, particularly when the knees or hips are affected.
To determine the extent of disabling, the referring physician and/or the surgeon will likely ask about walking distance, sporting ability, the need for walking aids, and the ability to perform self-care tasks such as dressing and bathing. Besides evaluation of the joint itself and level of mobility, the clinical examination will include evaluation of the patient's general health, the condition of the ligaments and muscles around the affected joint, and also assessment of the patient's mental outlook and social circumstances to help develop the most effective postoperative rehabilitation plan. Diagnostic testing will typically include:
x rays of the affected joint (and other joints as well)to determine loss of joint space and to differentiate between OA and RA
imaging studies, such as computed tomography (Cat scans), magnetic resonance (MRI), and bone densitometry to assess bone loss or bone infection
cardiac tests, such as electrocardiogram, to evaluate the heart and circulatory system
blood tests to rule out infection and possibly to confirm arthritis
It is a method by which the surgeon removes the damaged cartilage and bone and replaces it with new metal and plastic joint surface to repair the connection and painless functioning of joints.
Various conditions can produce joint pain and disability and direct patients to consider joint replacement surgery. In many cases, joint pain is produced either from arthritis, a fracture, or another condition.
General pre-operative instructions are as follows:
The basic instructions you should follow after your surgery are as follows:

Immediately after surgery, while still in the hospital, patients will be given pain medications for the recovery period and antibiotics to prevent infection. When patients are discharged after joint surgery, they must be careful not to overstress or destabilize the joint, requiring rest at home for a period of weeks. Physical therapy will begin immediately to improve strength and range of motion; it is the most important aid to recovery and may continue for several months. Activity may be resumed gradually, using devices if necessary, such as walkers or crutches, as recommended by the physical therapist. Lifestyle changes may include the use of special seating or sleeping surfaces, and employing home care assistance for help with shopping, cooking, and household tasks.
Joint resection and interpositional reconstruction do not always produce successful results, especially in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, a chronic inflammatory disease that may continue to narrow the joint space and accelerate the formation of scar tissue. Repeat surgery or total joint replacement may be necessary.
As with any major surgery, there is always a risk of an allergic reaction to anesthesia, post-operative infection, or the formation of blood clots (thrombophlebitis) that may cause pain and swelling near the surgery site and travel through the veins to other parts of the body. A joint that has undergone surgery is less stable than a healthy joint and dislocation or loosening of the resected joint may occur, especially with inappropriate physical activity.
Most patients enjoy an improved range of motion in the joint and relief from pain. Younger people may actually return to some form of low-impact sports activity. However, people who have degenerative or inflammatory diseases must understand that they will not suddenly have a normal joint, even while they will gain pain relief and improved function.
The number of deaths for all arthroplasty surgeries is less than 1%, with death more likely to occur among elderly patients and those with other serious medical conditions.

Pain management alone, particularly with the availability of more effective pain drugs that have fewer side effects, is the primary non-surgical option when the underlying diagnosis is a form of arthritis. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) are commonly prescribed for arthritis sufferers, and people with RA are given certain drugs that suppress immune system activity, shown to be a factor in this type of arthritis. A range of nutritional supplements and vitamins are reported to offer health benefits to people with OA; among them, glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate have been shown to offer some relief for pain and stiffness. Weight loss is often recommended as well.
Because immobility of the affected joint can increase pain and stiffness, patients with joint disease are usually encouraged to continue some type of physical activity. Keeping the muscles strong through modest, non-weight-bearing exercise , such as stretching or swimming, is often recommended to help support the joint and maintain mobility. Various devices, such as braces or orthopedic shoes, may be recommended, as well as walking aids. Safety rails, special elevated toilet-seat extensions, bath and shower seats can make the patient more comfortable in daily life. Movement therapy, such as yoga, tai chi, and dance, may help maintain joint flexibility and slow chronic arthritis symptoms. Occupational therapy, massage therapy, and physiotherapy may help improve range of motion and overall comfort, as well as patient confidence.